
Histograms very produced for the merged dataset ( i.e. all fields for which both XMM data and WFC i--band data were available) by calculating the likelihood ratios and reliabilities for each field and concatenating them.
The fields used were:

The role of reliability in exposing the few cases where the nearest object is
not the most likely is again visible in Fig. ![]() . Over the merged
sample of 607 sources, this happened for 18 sources.
. Over the merged
sample of 607 sources, this happened for 18 sources.
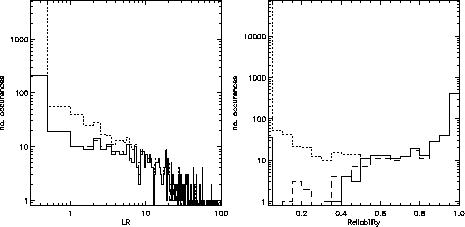
Figure: Histograms of a) likelihood ratio and b) reliability (S&S) for the Lockman Hole field. Dotted line: all candidates out to 50 arcsecs. Solid line: most likely candidate for each source. Dashed line: closest candidate for each source.
In Fig. ![]() these cases have been highlighted. The definition of
reliability provided by Sutherland & Saunders [6] provides a
powerful tool for detecting instances where the positional coincidence method
is insufficient.
these cases have been highlighted. The definition of
reliability provided by Sutherland & Saunders [6] provides a
powerful tool for detecting instances where the positional coincidence method
is insufficient.
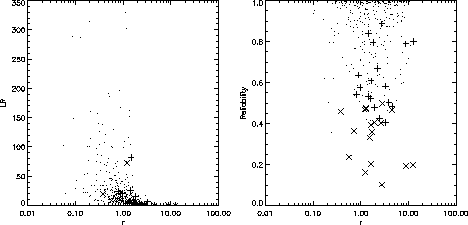
Figure: a) likelihood ratio and b) reliability (S&S) versus separation for the merged dataset. Dots: most likely candidate. +: most likely candidate if different from closest.  : closest candidate if different from most likely.
: closest candidate if different from most likely.
Fig. ![]() (a) shows that the most likely matches have a separation
of around 1 arcsec. However a significant number of associations with high
likelihood ratio and reliability have a separation larger than 5 arcsecs,
the optimal search radius identified using offset histograms, although they
all lie within 15 arcsecs.
(a) shows that the most likely matches have a separation
of around 1 arcsec. However a significant number of associations with high
likelihood ratio and reliability have a separation larger than 5 arcsecs,
the optimal search radius identified using offset histograms, although they
all lie within 15 arcsecs.